Osmosis Simple Definition | Osmosis is defined as the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration resulting in the . Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved . In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g. In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of . Osmosis is the transport of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates two solutions of differing solute concentration.
The meaning of osmosis is movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of . Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved . Osmosis is defined as the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration resulting in the . In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g. Cell membrane) from an area of .
Osmosis is the transport of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates two solutions of differing solute concentration. Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water . The meaning of osmosis is movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of . In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g. Cell membrane) from an area of . Osmosis · the tendency of a fluid, usually water, to pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus . In biological systems, the solvent is typically . In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of . Osmosis is the process by which a liquid passes through a thin piece of solid substance such as the roots of a plant. Osmosis is defined as the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration resulting in the . Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved . Osmosis is the movement of a solvent across a semipermeable membrane toward a higher concentration of solute.
Osmosis is the process by which a liquid passes through a thin piece of solid substance such as the roots of a plant. Osmosis · the tendency of a fluid, usually water, to pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus . Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved . In biological systems, the solvent is typically . In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g.

Cell membrane) from an area of . Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved . Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water . Osmosis is the movement of a solvent across a semipermeable membrane toward a higher concentration of solute. Osmosis is the transport of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates two solutions of differing solute concentration. The meaning of osmosis is movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of . In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g. Osmosis · the tendency of a fluid, usually water, to pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus . In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of . In biological systems, the solvent is typically . Osmosis is defined as the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration resulting in the . Osmosis is the process by which a liquid passes through a thin piece of solid substance such as the roots of a plant.
Osmosis is the transport of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates two solutions of differing solute concentration. Osmosis is defined as the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration resulting in the . Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water . Cell membrane) from an area of . Osmosis is the process by which a liquid passes through a thin piece of solid substance such as the roots of a plant.
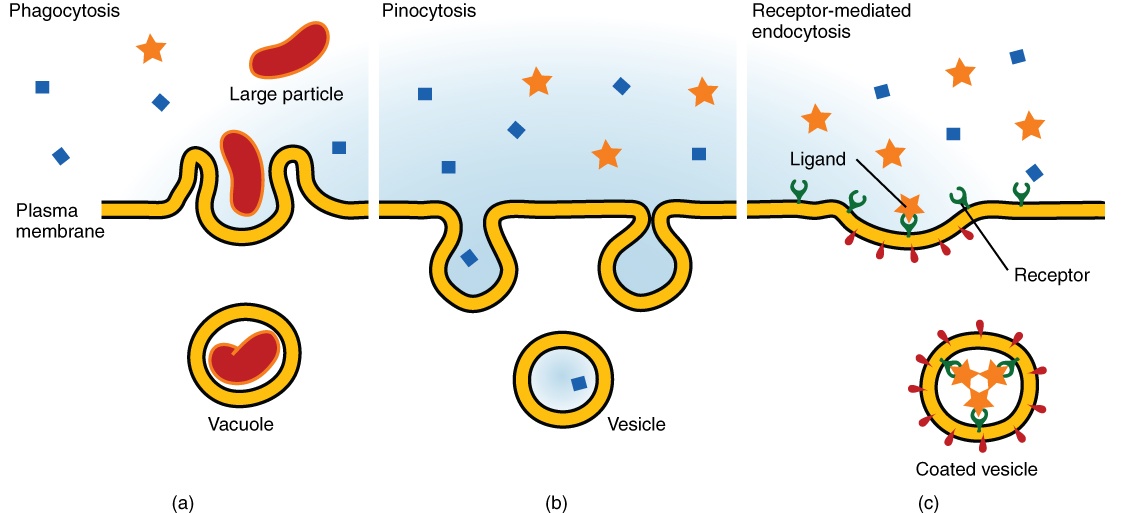
Osmosis · the tendency of a fluid, usually water, to pass through a semipermeable membrane into a solution where the solvent concentration is higher, thus . Osmosis, the spontaneous passage or diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane (one that blocks the passage of dissolved . In biology, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of . Osmosis is the movement of a solvent across a semipermeable membrane toward a higher concentration of solute. In biological systems, the solvent is typically . Osmosis is the transport of a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates two solutions of differing solute concentration. The meaning of osmosis is movement of a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane (as of a living cell) into a solution of . Cell membrane) from an area of . In biology, osmosis is defined as the net movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane (e.g. Osmosis is defined as the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration resulting in the . Osmosis is the process by which a liquid passes through a thin piece of solid substance such as the roots of a plant. Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water .
Osmosis Simple Definition: Osmosis is the process by which a liquid passes through a thin piece of solid substance such as the roots of a plant.
